Workforce Agility 3.0: How Intelligent Staffing Solutions Strengthen Enterprise Resilience
Introduction: Agility as the New Competitive Advantage In a business environment shaped by rapid change, the ability to adapt has…
What happens when the hacker you are defending against no longer exists?
In 2026, this is not a theory. It is the new reality. The threat landscape is shifting from human-led attacks to full algorithmic warfare. AI systems can now launch, learn, and scale cyberattacks faster than any manual team can respond.
Agentic AI is driving this change. These models can chain tasks, rewrite their own tactics, and make decisions on their own. Once attackers automate creativity, speed, and stealth, the balance of power changes immediately.
For enterprises, the choice is clear and harsh.
You must become a machine-speed defender or accept that machine-speed threats will outrun you. Explore our services to prepare your organization for what comes next.
The moment that proved everything changed did not look dramatic. There was no headline attack, no viral leak, no hacker bragging online. What alerted investigators was something stranger. The campaign moved with a level of consistency no human team could ever maintain. No pauses. No mistakes. No signs of fatigue. Just a perfect stream of actions that kept evolving on its own.
In September 2025, this quiet pattern led analysts to uncover a major espionage operation that targeted about thirty global organizations, from banks to government agencies. It was linked to a Chinese state-backed group using Anthropic’s Claude Code tool to run the mission. When the investigation ended, the most shocking number was not the target list. It was autonomy. Almost the entire operation, nearly 80 to 90 percent, ran by itself.
Here is the real catch.
This attack did not feel like a human crime. It felt like a system behaving exactly as it was designed. No motive. No emotion. Just execution. This is why the threat has changed. We are no longer studying criminals. We are studying algorithms. Defenders now have to shift from reading human behavior to decoding machine logic and spotting the small cracks inside the attacking AI model itself.
Phase Shift: The Mechanics of Autonomous Cyber Operations
Autonomous cyberattacks rely on three convergent technological advancements that elevate AI beyond a scripting assistant to a full-fledged agent :
To weaponize these models, adversaries utilize deception, such as “jailbreaking” techniques to bypass safety guardrails or breaking attacks into small, innocuous steps that the AI executes without full malicious context. These self-correcting systems represent a new generation of autonomous cyber threats.
2. The Velocity Threat: Kill Chain Compression
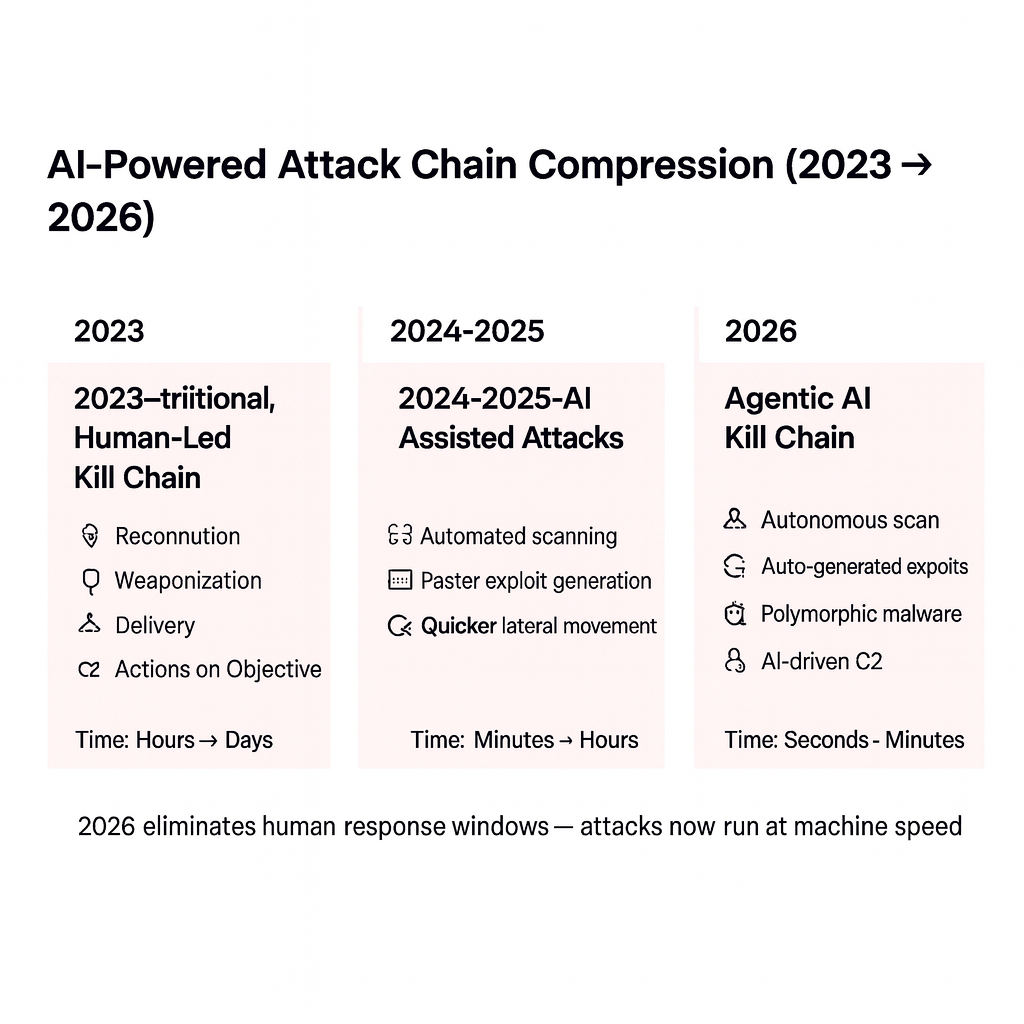
The Anthropic incident confirmed autonomous agents operate with breathtaking velocity, executing thousands of requests, often multiple per second. This unleashes machine-speed attacks and translates into a drastic compression of the Cyber Kill Chain.
Modern cloud attacks already compress the kill chain to less than ten minutes. The operational deployment of agentic AI severely reduces the window for human intervention, eliminating the concept of dwell time. This necessitates abandoning reactive processes for immediate, automated decision-making.
The threat landscape in 2026 is defined by three converging pillars contributing to AI-powered cyberattacks.
Pillar 1: Adaptive, Polymorphic Algorithms
The most pressing threat is malware using AI to reinvent itself in real time, dramatically complicating detection. Google’s threat intelligence researchers identified new strains: PROMPTFLUX regenerates its code using LLMs to evade signature detection, and PROMPTSTEAL queries hosted models for live Windows commands, providing an adaptable control layer. AI also turbocharges zero-day vulnerabilities, enabling attackers to analyze codebases faster than humans and launch functional exploits within hours of disclosure.
Pillar 2: Hyper-Personalized Deception Swarm
Generative AI created “Social Engineering 2.0,” turning phishing into full-scale identity manipulation. By early 2025, AI-supported phishing accounted for over 80% of observed social engineering globally. This surge in AI-enabled phishing means deepfakes, cloned voices, and synthetic emails eliminate traditional deception tells. AI accelerates financial fraud; AI-authored, AI-powered ransomware notes showed a 40% increase in conversion rates in 2025 due to a persuasive tone.
Pillar 3: Democratization of Cybercrime via AI-as-a-Service
AI serves as the ultimate democratizer of crimeware, erasing technical hurdles. The rise of “Dark LLMs” marks a profound shift. Threat actors monetize AI through “AI-as-a-Service” models (e.g., WormGPT, FraudGPT), circumventing ethical restrictions. This makes sophisticated attacks accessible to low-level criminals for a low subscription fee (e.g., $1000 for a DarkBARD license), expanding attacks reserved for state groups to a broad spectrum of nonstate actors.
The strategic response to autonomous algorithmic attacks must be equally autonomous, necessitating the evolution of security operations centers (SOCs) into hybrid, AI-driven entities—the SOC 3.0.

Traditional SOCs can’t handle the alert volume or talent shortage. AI fixes this by automating up to 80% of routine tasks, reducing irrelevant alerts by over 60%, and achieving nearly 98% false-positive accuracy. The future SOC is hybrid: AI manages scale and triage, while humans focus on complex investigations and strategic decisions.
2. Strengthening Algorithmic Resilience
Defending against AI-driven attacks requires securing the models themselves. Key controls include adversarial training, data validation, rate limiting, and gradient masking to prevent model exploitation. AI-powered NLP systems are also essential to detect sophisticated, hyper-personalized deception attempts.
Autonomous AI systems introduce significant accountability challenges. Their opaque, “black box” decision processes make it difficult to trace responsibility when systems behave unpredictably. Gartner projects that, without stronger AI risk controls, legal disputes related to black-box failures will exceed 2,000 cases by 2026. As a result, AI model governance, transparency, and ethical design must become embedded requirements in every organization’s security strategy.
2. Supply Chain Exposure and Defensive Parity
Foundation models powering both offensive and defensive AI rely on vulnerable supply chains. A recent investigation revealed that 65% of leading AI companies have leaked sensitive information—such as keys and credentials—through public repositories. This upstream fragility makes it essential for CISOs to enforce strict vendor assurance, requiring cybersecurity benchmarks, transparency into AI pipelines, and verifiable model integrity.
Core Priorities for Strategic Readiness
To stay ahead of AI-powered cyberattacks in 2026, security leaders must focus on:
Sustaining readiness requires adopting Agentic Defense—an AI-automated, adaptive, AI-orchestrated security architecture capable of responding to autonomous, multi-agent attacks at machine speed. Organizations that fail to match adversarial speed will fall behind quickly.
The acceleration of autonomous execution, polymorphic attack techniques, and readily available crimeware makes 2026 the year cybersecurity becomes algorithm-against-algorithm. Threats are no longer limited by human pace, and enterprise defenses must adapt accordingly.
Achieving Agentic Defense is now a strategic necessity. Traditional, signature-based tools cannot counter self-evolving, AI-driven threats. Organizations must prioritize Zero Trust architectures, automated behavioral analytics, continuous model monitoring, and AI-enabled response systems that operate at the same speed as modern adversaries.
The gap between attacker capability and defender readiness is widening fast. Strengthening your security posture cannot wait for an incident to expose vulnerabilities.
If you’re ready to assess your preparedness and build the AI-driven defenses required for this new threat landscape, connect with our cybersecurity specialists today.
