The Skills Wars: Why Degrees Are Losing and Skills Are Winning in 2025
Introduction Degrees might get you noticed — but skills seal the deal. Across industries, leaders are shifting focus from pedigree…
What if the biggest threat to your cybersecurity program is not an attacker, but your own budget plan?
2026 is the year many security teams will face that uncomfortable truth. Spending is rising fast. Forrester expects global cybersecurity investments to hit 174.8 billion dollars in 2025. But the problem is not the size of the budget. The problem is that most of it is still tied to tools that no longer protect the enterprise.
Geopolitical conflict is increasing. Agentic AI is rewriting the threat landscape. Digital ecosystems are expanding faster than they can be secured. These pressures are creating three giant waves that will hit every organization: Identity, Supply Chains, and Quantum. Each one brings a level of risk that legacy controls cannot manage. This is why 2026 requires a shift from old habits to modern resilience.
In this blog, we explore how these waves are reshaping cyber budgets and what security leaders must focus on to stay in front. If your organization is preparing for this shift, our Cybersecurity Strategy and Governance services can help you accelerate readiness and build stronger defenses for the future.

Identity has quietly become the front door to the entire enterprise, and attackers know it better than anyone. The numbers prove it. One in every five breaches starts with a stolen or misused credential. When you widen the lens to the full human element, like phishing, wrong logins, or simple mistakes, the number jumps to eighty-two percent. It is the clearest sign that traditional perimeter security is no longer protecting what matters.
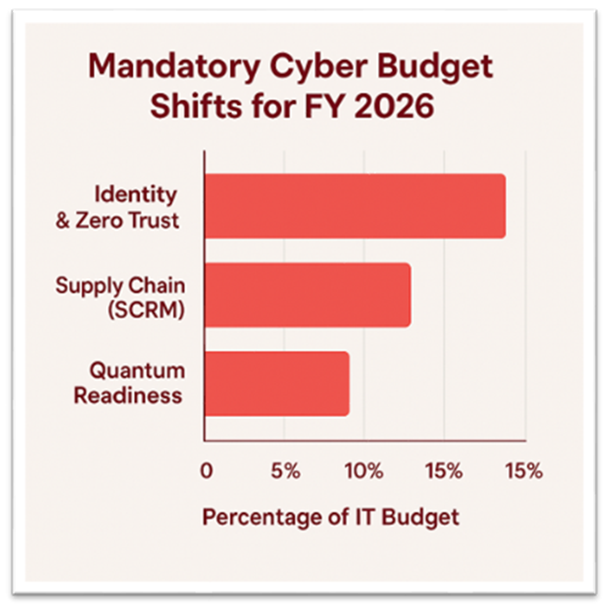
This is why global benchmarks now push organizations to invest ten to fifteen percent of their IT budgets into identity controls guided by the CISA Zero Trust model, NIST CSF 2.0, and micro-segmentation programs. These are not abstract frameworks. They deliver real results. Companies with strong identity controls have reported up to forty-five percent lower breach costs. The message is simple. In a world where attackers enter through the login more than the network, identity is no longer a tool. It is the anchor of the entire 2026 cybersecurity budget.
Identity risk is escalating due to the explosive growth of machine identities, which now outnumber humans 82:1 across cloud and AI environments. Generative and agentic AI systems are rapidly creating new privileged identities, often with sensitive access rights, thereby dramatically expanding the attack surface. Analysts warn that a poorly governed AI identity could trigger a significant breach, highlighting the need to secure machine intent and automated access paths under Zero Trust principles.
A significant shift in identity budgets will also come from transitioning to password-less authentication. Although implementation costs $300,000–$450,000, enterprises achieve ROI in 6–18 months as helpdesk workload and credential-related incidents drop. Traditional passwords cost $50,000–$100,000 annually in support and up to $500,000 per breach. Passwordless systems cut these costs by 40–80%, converting volatile OpEx into a predictable security investment.
For 2026, CISA’s mandate is clear: adopt phishing-resistant WebAuthn/FIDO2 for all privileged accounts to establish identity as the foundational layer of Zero Trust.
The vulnerability of the extended enterprise requires Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM) programs to be fundamentally restructured and sufficiently funded in 2026. This urgency is driven by the explosive growth in third-party-related breaches, where vendor involvement in incidents doubled year-over-year, climbing from 15% to 30%.6 Global regulatory mandates are now translating this threat into mandatory budget lines.
Global Mandates and the Cost of Transparency
Two major regulations are redefining software assurance and making supply chain security a mandatory budget line for 2026:
Together, these regulations make the Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) a legal requirement. CISA’s updated SBOM minimum elements in 2025 further increase transparency expectations.
Cyber Budgets 2026 must fund:
This is no longer a niche compliance expense — it is now a core operational investment. Legal, procurement, and security teams will need sustained funding to enforce vendor transparency and run mature SCRM programs. Organizations can strengthen readiness through Compunnel’s Cyber Strategy & Governance services, ensuring supply chain security evolves into a proactive, audit-ready capability.
The Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) challenge requires immediate, substantial budget allocation due to the risk of “Harvest Now, Decrypt Later” attacks, where encrypted data is stolen today and stored for decryption once capable quantum computers become available. Post-Quantum Cryptography spending is expected to move squarely into the enterprise mainstream in 2026. According to Forrester’s Predictions 2026, quantum security spending will surpass 5% of total IT security budgets as organizations prepare for this future.
This significant spending is driven by a non-negotiable regulatory timeline set by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), which plans to deprecate quantum-vulnerable RSA and ECC cryptography by 2030 and fully prohibit them by 2035. Security teams must secure an approved budget, governance plan, and dedicated team by Q2 2026 to remain on track for this multi-year infrastructure transition.
PQC preparation starts with cryptographic discovery—locating all vulnerable encryption across networks, applications, databases, IoT devices, and SCADA systems.
Organizations must then create a Cryptographic Bill of Materials (CBOM) using automated tools to identify quantum-vulnerable algorithms and the data they protect.
The final requirement is crypto-agility, enabling rapid updates to cryptographic libraries and seamless shifts to new PQC standards, often through hybrid approaches.
These efforts will consume 5%+ of IT security budgets in 2026 and must be treated as a major infrastructure program. Migrating legacy systems and embedded devices is complex and costly; delaying investment past mid-2026 will make remediation rushed, more expensive, and risk non-compliance with PCI DSS 4.0, HIPAA, and GDPR.
The Mandatory Cyber Budget Shifts for FY 2026
| Tsunami Wave | Primary Financial Driver (2026) | Compliance/Mandate Focus | Key Strategic Investment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identity & Zero Trust | 10–15% of IT Budget allocation | CISA Zero Trust Directive, Password-less Migration | Phishing-resistant MFA, Micro-segmentation tools |
| Supply Chain (SCRM) | Doubled Third-Party Branch Involvement (15% to 30%) | EU Cyber Resilience Act (CRA), US EO 14028 (SBOM) | SBOM Generation/Analysis Tools, Continuous TPRM |
| Quantum Readiness | >5% of IT Security Budget | NIST PQC Roadmap (2030 Deprecation) | Cryptographic Discovery (CBOM), Crypto-agility solutions |
Cyber Budgets 2026 require a fundamental reallocation of resources toward resilience. With breach costs rising nearly 10% year-over-year, security leaders can no longer justify spending on legacy perimeter tools that fail against modern threats. The combined pressures of identity-driven attacks, global supply chain transparency mandates, and the urgent timeline for quantum-safe encryption make proactive investment far more cost-effective than reactive mitigation.
The path forward is clear:
Organizations that make these shifts now will be positioned to withstand advanced, multi-vector attacks while maintaining operational continuity.
If you’re planning your 2026 cyber investments, our team can help you prioritize the highest-impact controls and build a long-term resilience roadmap. Start your transformation with our [Cybersecurity Strategy & Governance services].
