Why Global Employer of Record (EOR) Companies are the Backbone of Remote Work
Introduction: The Hidden Cracks in the Remote Work Dream According to a recent Remote.com report, nearly 50% of global payroll…
The manufacturing industry is facing a silent storm—one that isn’t just about automation, supply chain disruptions, or global competition. It’s about people, or more precisely, the inability to keep them.
Gen Z, the newest generation in the workforce, is rewriting the rules of employment. Traditional notions of loyalty, tenure, and slow career progression no longer resonate with them. Instead, their approach is fluid—prioritizing personal growth, skill-building, and instant gratification over long-term commitment to a single employer.
The result? A talent retention crisis that manufacturing was never prepared for. Unlike white-collar sectors that can embrace hybrid models and remote flexibility, manufacturing relies on on-site, skilled labor—making frequent job exits a costly disruption.
The industry is scrambling for solutions, but the real question is: Are manufacturers ready to change their hiring and retention playbook?
This blog dives deep into why Gen Z is job-hopping at unprecedented rates, what it’s costing the industry, and how forward-thinking companies are turning AI-powered recruitment strategies into a competitive advantage.
Manufacturing has always been built on stability—long-term careers, specialized skills, and a workforce that grows with the company. But with Gen Z, that stability is disappearing fast.
Welcome to the ‘Quick Quit’ era.
A growing number of young workers in manufacturing are quitting within their first few months, leaving employers scrambling to refill positions. Unlike previous generations who prioritized stability and tenure, Gen Z approaches jobs like a test drive—if it doesn’t feel right early on, they move on. According to a LinkedIn Workforce Report, Gen Z employees are switching jobs 134% more than they did pre-pandemic, making turnover a pressing challenge. The urgency is even greater in manufacturing, where the average retention rate for young workers has now dropped below that of retail, a sector long known for high churn.
A survey by HR Dive found that 80% of Gen Z employees decide within 60 days whether they’ll stay long-term or start looking for their next job. This shortened decision window is forcing manufacturers to rethink onboarding, career progression, and workplace culture before they lose talent to more adaptable industries.
Gen Z evaluates their employer faster than any previous generation. If the first two months don’t meet their expectations, whether it’s job training, work culture, or growth opportunities—they mentally check out long before submitting their resignation.
-How It Affects Manufacturing: Many factories and production facilities still operate on outdated onboarding processes that focus on compliance and procedures rather than engagement and career development. For Gen Z, this feels transactional, not inspiring.
Unlike Baby Boomers and Gen X, who often spent decades at a single company, Gen Z isn’t loyal to employers—they’re loyal to skills.
What does this mean:
– How It Affects Manufacturing: Many entry-level roles in manufacturing are highly specialized but lack clear career growth pathways. Without structured, fast-paced upskilling programs, Gen Z workers feel stuck—and they leave.
Gen Z is not just motivated by salary—but that doesn’t mean they’ll stay if pay isn’t competitive. They evaluate job offers based on total career value:
If the answer to any of these is “no,” they start planning their exit strategy.
– How It Affects Manufacturing: Many manufacturing companies still follow rigid promotional structures that require employees to spend years in the same role before advancing. Gen Z expects faster career milestones and visible growth opportunities.
Manufacturing has long been an industry where expertise, tenure, and operational efficiency go hand in hand. But with Gen Z leaving faster than ever, the financial strain of high turnover is becoming a silent crisis. Annual turnover rates in manufacturing have exceeded 40%, meaning some companies are cycling through half their workforce every year, creating a continuous disruption in operations. Every time a young worker quits, manufacturers aren’t just losing an employee—they’re bleeding resources, productivity, and competitive advantage. According to Deloitte’s 2024 report, high turnover is now one of the top three reasons manufacturing companies struggle to meet production goals, further amplifying the urgency for a workforce retention overhaul.
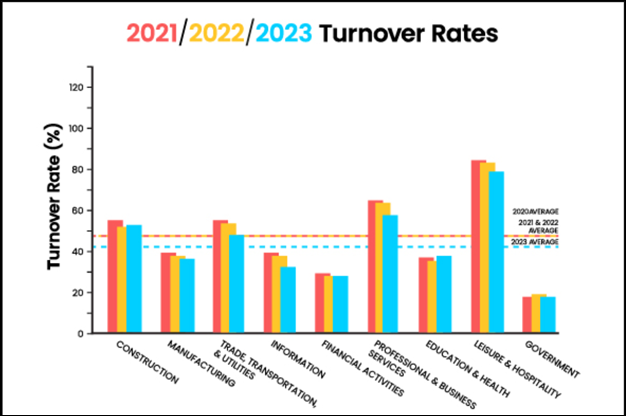
While many companies focus on recruiting expenses, the real losses go beyond hiring fees:
A study by the Work Institute found that U.S. businesses collectively lose over $1 trillion annually due to employee turnover. For manufacturing, where efficiency is key, these losses directly impact profit margins.
The talent shortage in manufacturing is already a major issue. With Gen Z leaving faster than they can be replaced, the skills gap is growing at an alarming rate.
The longer manufacturers ignore this issue, the harder it will be to recover.
To fight job-hopping, many manufacturers have tried raising salaries and offering sign-on bonuses. But this quick fix isn’t sustainable—and here’s why:
A recent SHRM report found that manufacturers who increased wages without improving career paths saw no significant drop in attrition. The reality? Gen Z isn’t just quitting for money—they’re quitting because manufacturing isn’t meeting their expectations.
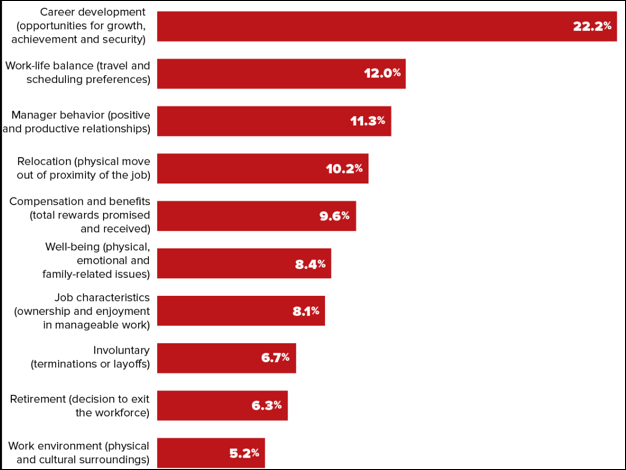
The Hard Truth: Manufacturing Must Rethink Talent Strategy
If manufacturers continue to treat Gen Z turnover as a recruitment issue rather than an economic crisis, they’ll keep losing money, talent, and industry relevance.
So, what’s the solution?
Manufacturers need to fundamentally rethink workforce retention—shifting from compensation-driven hiring to AI-powered career mobility, skills development, and workplace reinvention.
The next section will dive into how forward-thinking manufacturing companies are implementing bold strategies to retain Gen Z talent—before it’s too late.
Manufacturers are facing a turnover crisis, but throwing money at the problem isn’t enough. Gen Z doesn’t just want a paycheck—they want career growth, workplace flexibility, and a sense of purpose.
So how can manufacturers adapt, retain, and engage this new workforce?
Here’s a playbook of strategies that actually work—moving beyond outdated hiring models and building workplaces where Gen Z thrives.
The old approach? Linear career progression.
The new approach? ‘T-Shaped’ career mobility.
Some manufacturers have introduced rotational programs that let Gen Z workers try different departments before committing to a specific role—reducing turnover by up to 30%.
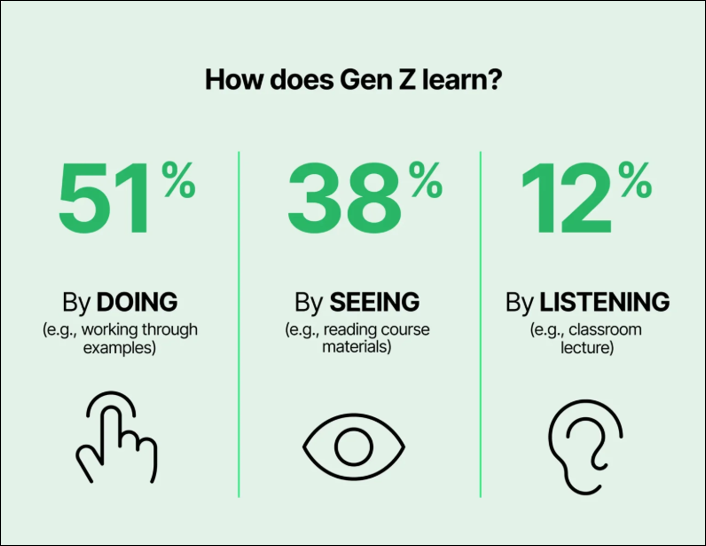
Gen Z’s mindset:
Instead of relying on traditional promotions every 3-5 years, manufacturers need to implement micro-promotions—frequent, small career milestones that keep Gen Z engaged.
What This Looks Like in Action:
Why It Works:
A study by McKinsey found that companies with structured micro-promotions had 40% lower Gen Z attrition rates compared to companies using traditional promotion cycles.
Manufacturing jobs have traditionally been rigid and location-based, making them less appealing to Gen Z compared to remote-friendly industries.
The Solution? A ‘Flex-Stability’ Work Model.
How It Works:
Why This Matters:
Some manufacturers have implemented AI-powered scheduling tools that give employees more control over their shifts, reducing last-minute attrition.
Traditional hiring models focus on experience and qualifications—but that’s not enough. Culture fit is now the #1 predictor of retention.
How AI is Changing Retention:
The Impact:
A major automotive manufacturer implemented AI-driven retention modeling and reduced early turnover by 30% within a year.
Manufacturers still struggle with a shrinking talent pool, and many over-prioritize formal education when hiring. But Gen Z values skills over degrees.
The Shift Towards Skills-Based Hiring:
Companies like Tesla and Boeing have reduced reliance on traditional degrees and launched specialized training programs to attract and retain Gen Z workers.
Manufacturing’s Gen Z retention problem isn’t just about hiring more people, it’s about hiring the right people and keeping them engaged from day one. Traditional HR strategies aren’t keeping up with Gen Z’s expectations, but AI-powered talent solutions are stepping in to bridge the gap.
Here’s how Compunnel Talent Solutions is redefining workforce retention using AI-driven hiring, predictive analytics, and smart workforce engagement.
What It Does:
Why It Works:
The Problem with Traditional Hiring:
How Compunnel Solves It:
Why This Matters:
The Challenge:
How Compunnel is Changing the Game:
Why It Works:
The Problem:
The Compunnel Solution:
Why It Works:
Manufacturers can’t afford to keep using outdated hiring and retention strategies. Gen Z isn’t leaving jobs just for higher pay—they’re leaving for better career experiences. Job-hopping is no longer just a workforce trend—it’s an economic crisis for manufacturers. High hiring costs, skill gaps, and lost productivity are already impacting profitability. Companies that continue relying on traditional recruitment and rigid promotion models will struggle to compete in an industry where agility and talent sustainability are now business imperatives.
The manufacturing sector must rethink its talent retention approach—shifting from mass hiring to AI-driven talent matching, predictive workforce engagement, and structured career pathways. Investing in real-time workforce analytics, culture-fit hiring, and reskilling initiatives will not only reduce turnover but also help manufacturers build a workforce that grows with the company instead of outgrowing it. Organizations that embrace these changes will attract, retain, and develop a Gen Z workforce that stays, contributes, and evolves within the industry.
Compunnel Talent Solutions is enabling manufacturers to navigate this shift with AI-powered hiring models, retention-focused workforce strategies, and career-mobility solutions. The future of manufacturing depends on building an engaged, adaptable workforce—one that doesn’t just fill jobs but drives innovation and long-term business success.
Get ahead of the retention crisis. Let’s build a smarter workforce today.
